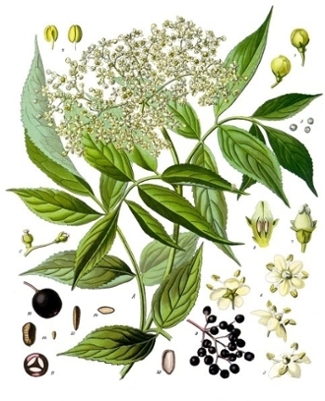
Safety/Precautions:
- Even though various herbal products made from Black Elder flowers have not shown any toxicity, they have not been thoroughly evaluated during pregnancy and lactation.
- Slight gastrointestinal discomfort is one of the possible side effects.
- Parts of Black Elder (especially the roots, bark, leaves, and green or unripe berries) can be potentially toxic.
- Avoid ingestion, especially by small children.
Before you decide to take any medicinal herb or herbal supplement, be sure to consult with your health care professional first. Avoid self-diagnosis and self-medication: Always be on the safe side!